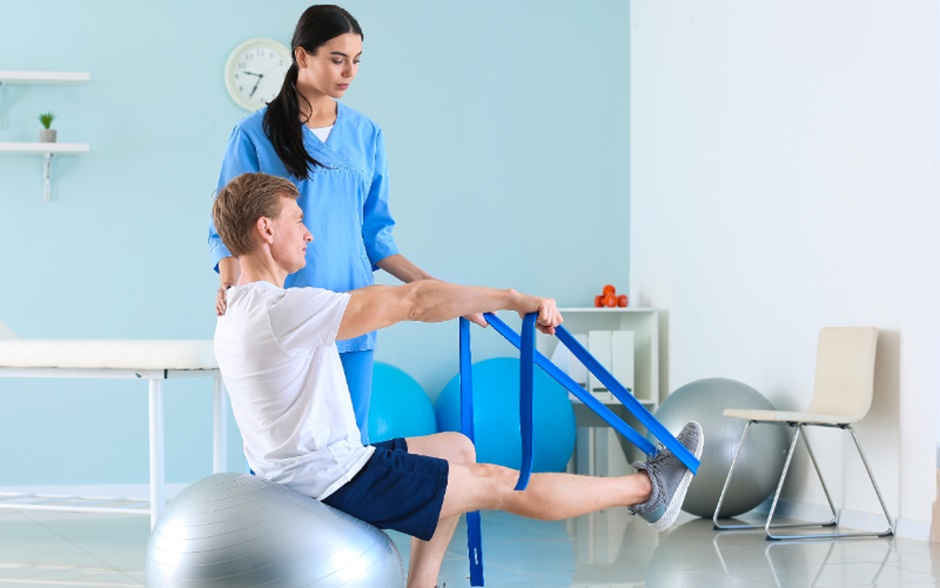
Non-surgical treatment options for knee joint pain offer viable alternatives to invasive procedures, aiming to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility without surgery. However, several common mistakes can hinder the effectiveness of these treatments. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for optimising outcomes in musculoskeletal physiotherapy and chronic muscle tension treatment.
Over Reliance on Pain Medications
One of the most common mistakes in treating knee joint pain non-surgically is overreliance on pain medications. While medications such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation and pain, they do not address the underlying causes of knee pain. Relying solely on medications without incorporating comprehensive treatment plans that include physiotherapy and targeted exercises can delay recovery and potentially mask worsening conditions.
Ignoring Muscle Imbalances and Weakness
Muscle imbalances and weaknesses around the knee joint are often overlooked but can significantly contribute to knee pain and instability. Neglecting to address these issues through targeted musculoskeletal physiotherapy and muscle strain treatments can hinder rehabilitation efforts. Strengthening muscles such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles through specific exercises prescribed by a physiotherapist is essential for restoring joint stability and reducing pain.
Skipping Physical Therapy Sessions
Skipping or inconsistently attending physical therapy sessions is another common mistake that can impede progress in non-surgical knee pain treatment. Physiotherapy plays a critical role in improving joint function, range of motion, and strength through tailored exercises and manual techniques. Patients who fail to adhere to their prescribed physiotherapy regimen may experience slower recovery times and may not achieve optimal outcomes in chronic muscle tension treatment.
Inadequate Rest and Recovery
Inadequate rest and recovery can exacerbate knee joint pain and prolong healing times. Engaging in high-impact activities or failing to allow sufficient time for tissues to heal can lead to further strain and inflammation. Rest is crucial for tissue repair and reducing stress on the knee joint. A comprehensive treatment plan should include periods of rest interspersed with appropriate exercises and activities recommended by a healthcare professional specialising in non-surgical treatment for knee joint pain.
Delaying Seeking Professional Treatment
Delaying seeking professional treatment for knee joint pain is a mistake that can worsen the condition over time. Early intervention with a healthcare provider experienced in musculoskeletal physiotherapy and non-surgical treatments is crucial for diagnosing the underlying cause of knee pain and implementing effective treatment strategies. Prompt treatment can prevent the progression of knee conditions and improve long-term outcomes for patients seeking relief from chronic knee pain.
Not Addressing Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as weight management, nutrition, and ergonomic considerations can significantly impact knee joint health and pain management. Excess weight places added stress on the knee joint, exacerbating pain and limiting mobility. A balanced diet rich in nutrients that support joint health, combined with ergonomic adjustments to reduce joint strain during daily activities, can complement non-surgical treatments and enhance overall outcomes for patients undergoing treatment for knee joint pain.
Lack of Patient Education and Compliance
Patient education and compliance with treatment recommendations are crucial for successful outcomes in non-surgical knee joint pain treatment. Failing to educate patients about their condition, treatment options, and the importance of adhering to prescribed therapies can lead to misunderstandings and poor treatment adherence. Healthcare providers specialising in chronic muscle tension treatment should prioritise patient education, ensuring that patients understand their role in managing knee joint pain and achieving long-term joint health.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common mistakes in non-surgical treatment for knee joint pain is essential for optimising outcomes and improving the quality of life for patients. By addressing underlying issues through targeted musculoskeletal physiotherapy, muscle strain treatments, and comprehensive rehabilitation plans, healthcare providers can help patients effectively manage knee pain and regain function without the need for surgery. With a proactive approach to treatment and patient-centred care, individuals experiencing knee joint pain can achieve lasting relief and maintain joint health for years to come.
Contact ProRehab today for more information.